内存层级
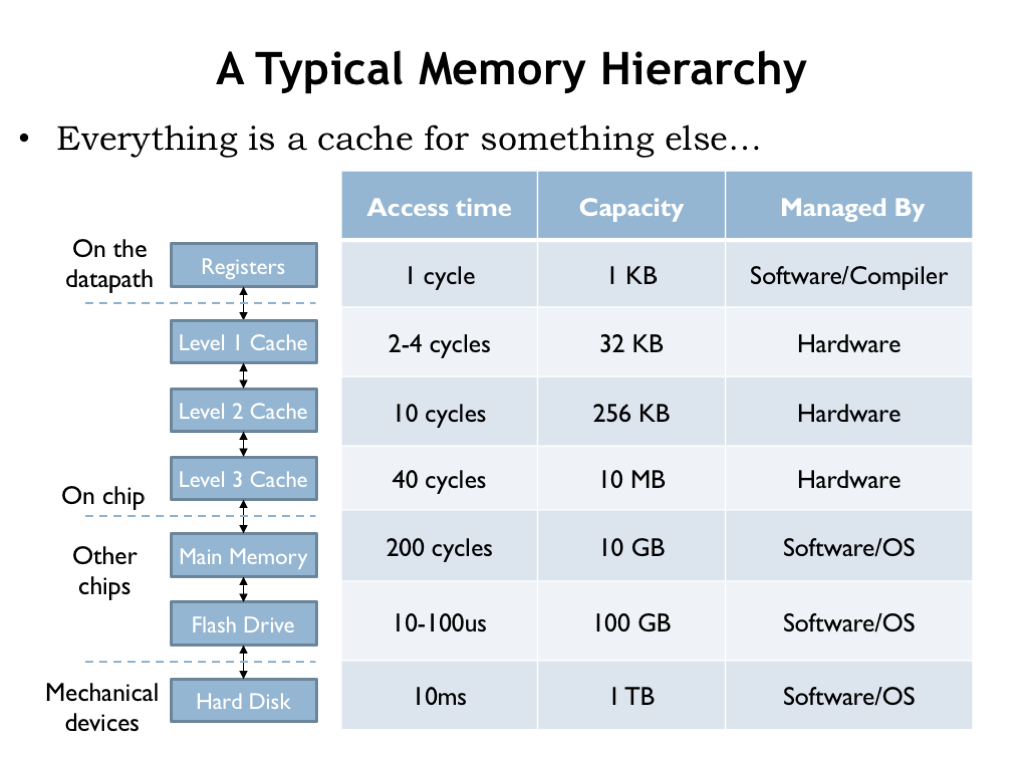
- Register
- Cache(L0-L4)
- RAM
- Hard Disk
操作系统内存管理
- Relocation caused by Swapping & Compaction
- Protection 进程地址空间隔离
- Organization
- Physical
- Logical
- Sharing
内存交换
当可用内存不足时,操作系统为了保证当前运行的程序正常执行,会将某些程序从内存中暂时移除放到二级存储(硬盘等)内
现代操作系统基本都支持内存交换
Linux 有单独的 swap partition Windows和macOS都是用Swap File(windows: Swapfile.sys macOS: /private/var/vm/swapfile*)
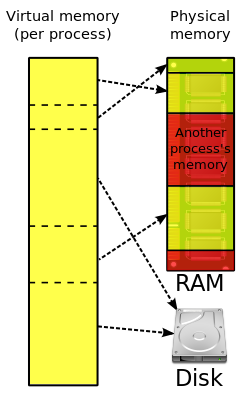
地址空间(Address Space)
每个进程独立的虚拟内存地址空间
- Low Memory (操作系统占用)
- High Memory (用户进程)
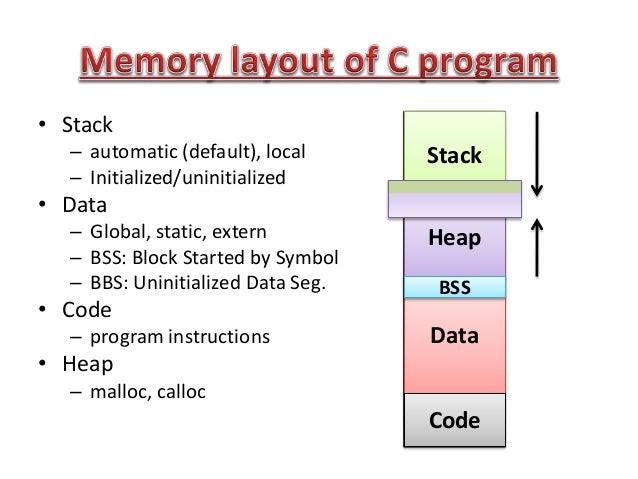
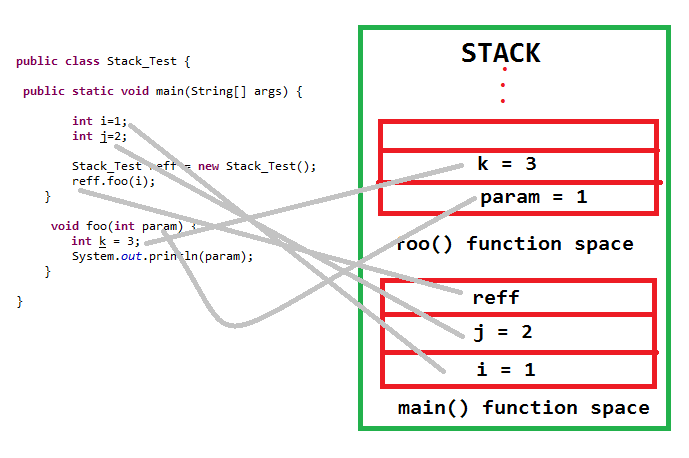
编程语言内存模型
虚拟内存(Virtual Memory)
对物理内存的抽象,可以大于实际可用物理内存。现代操作系统基本都提供虚拟内存功能,CPU在执行代码时通过MMU(Memory Management Unit)将虚拟内存地址转换成物理内存地址。
内存分配更简单高效
比实际可用物理内存更大的内存空间
减少外部碎片,更高的内存利用率
内存交换效率更高
Allocating memory is easy and cheap
Any free page is ok, OS can take first one out of list it keeps
Eliminates external fragmentation
Data (page frames) can be scattered all over PM
Pages are mapped appropriately anyway
Allows demand paging and prepaging
More efficient swapping
No need for considerations about fragmentation
Just swap out page least likely to be used
连续内存分配
给进程分配一块连续的内存
Partitions were used mainly on batch systems
Single Partition Embedded system
Multiple Partition 需要隔离
分割(Partition)
- Equal-Size Partition
- internal fragment
- Unequal-Size Partition
- Dynamic Partition
- external fragment
- Buddy System
- Equal-Size Partition
放置(Placement Algorithm)
- Best fit,choose smallest hole
- First fit,choose first block from beginning
- Next fit,choose first block from last placement
- Worst fit,choose largest hole
压缩(compaction)
非连续内存分配
将物理内存切分成很多小块(frames),把虚拟内存也切分成很多小块(segements/pages),然后进行映射。就不用给程序分配一整块连续的物理内存了。
分段(Segmentation)
divide virtual address space into variable-sized frames

分页(Page)
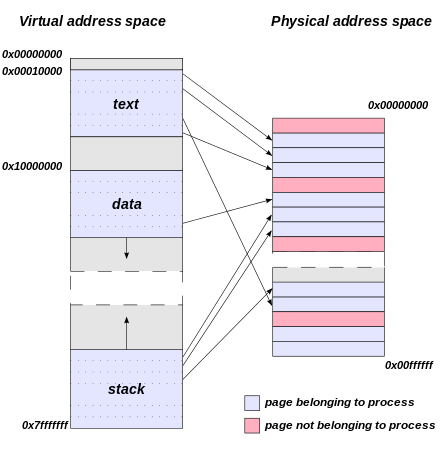
divide virtual address space into equal-sized frames
paging is implemented by integrating the hardware and operating system
- page 512b(扇区大小)~8192b
- page table
- 分层(hierarchy)
- 哈希表(hashed)
- 翻转(inverted), use physical frame to track page
- frame 物理内存切片 大小同page
- frame table
置换算法
- FIFO
- Optimal Page Algorithm
- Page Buffering Algorithm
- LRU(least recent use)
- LFU(least frequent use)
- MFU(most frequent use)
分段分页对比
- Segmentation requires more complicated hardware for address translation
- Segmentation suffers from external fragmentation
- Paging only yield a small internal fragmentation
- Segmentation is visible to the programmer whereas paging is transparent
- Segmentation can be viewed as commodity offered to the programmer to organize logically a program into segments and using different kinds of protection (ex: execute-only for code but read-write for data)
参考资料
- Memory management (operating systems)
- Memory management
- Introduction to Memory Management
- Memory Protection
- Thrashing
- before memory was virtual - the denning institute
- The Linux kernel user’s and administrator’s guide » Memory Management
- https://www.zhihu.com/question/50796850
- https://ocw.snu.ac.kr/sites/default/files/NOTE/3625.pdf
